How To Find Errors In Windows 10
How to check your drive for errors in Windows 10
July 2, 2015 07:22 / / Geek Tips Comments (ii)
Updated July 20, 2020
Keeping the drive in your Windows 10 computer error-gratuitous is essential to its operation. If y'all are experiencing issues opening files or applications, information technology may exist time to check your drive for errors. Hither is how to check your drive for errors in Windows 10.

There are ii ways of checking drives for errors in Windows ten, standard and advanced. The standard approach is the easiest to use, but the avant-garde method has more options.
Standard drive error checking in Windows 10
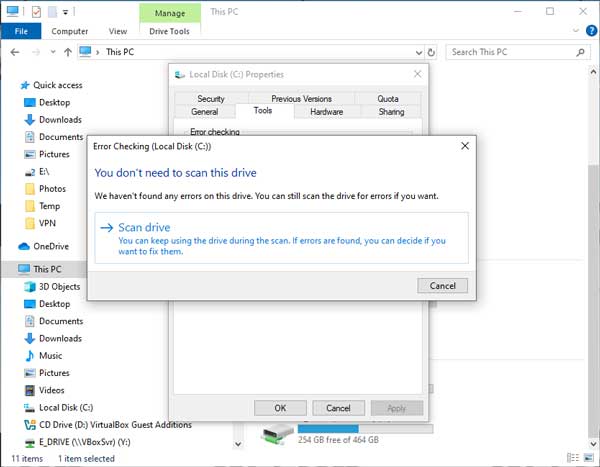
- Open File Explorer using one of the following:
- In the left-side column left-click on This PC.
- In the right-side cavalcade right-click on the drive you want to check and select Properties.
- Left-click on the Tools tab.
- Nether Error checking left-click on Bank check.
- Left-click on Scan drive.
Advanced drive error checking in Windows 10
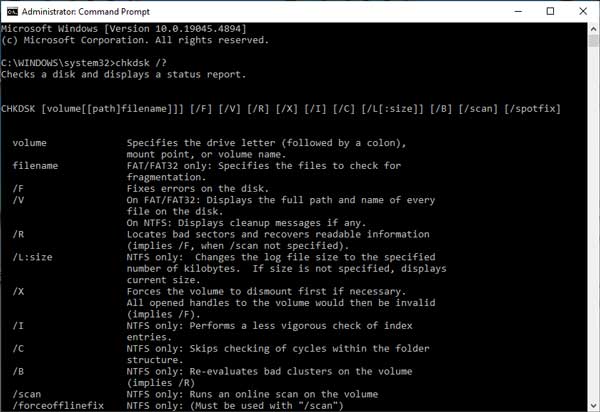
- Open up a Command Prompt with Administrative privileges (click here for instructions)
- Utilize the following command-line syntax(s) and parameter(s) to run CHKDSK:
CHKDSK [volume[[path]filename]]] [/F] [/V] [/R] [/X] [/I] [/C] [/50[:size]] [/B] [/browse] [/spotfix]
| volume | Specifies the bulldoze alphabetic character (followed by a colon), mount point, or volume proper name. |
| filename | FAT/FAT32 just: Specifies the files to check for fragmentation. |
| /F | Fixes errors on the deejay. |
| /V | On FAT/FAT32: Displays the full path and proper noun of every file on the disk. On NTFS: Displays cleanup messages, if whatever. |
| /R | Locates bad sectors and recovers readable information (implies /F, when /browse not specified). |
| /50:size | NTFS but: Changes the log file size to the specified number of kilobytes. If a size is non specified, it displays the electric current size. |
| /X | Forces the volume to dismount first if necessary. All opened handles to the book would so be invalid (implies /F). |
| /I | NTFS merely: Performs a less vigorous check of index entries. |
| /C | NTFS only: Skips checking of cycles within the folder structure. |
| /B | NTFS only: Re-evaluates bad clusters on the volume (implies /R). |
| /browse | NTFS only: Runs an online scan on the volume. |
| /forceofflinefix | NTFS just: (Must be used with "/browse") Bypass all online repair; all defects found are queued for offline repair (i.e. "chkdsk /spotfix"). |
| /perf | NTFS only: (Must be used with "/scan") Uses more system resources to complete a browse as fast equally possible. This may have a negative operation impact on other tasks running on the system. |
| /spotfix | NTFS only: Runs spot-fixing on the volume. |
| /sdcleanup | NTFS only: Garbage collects unneeded security descriptor data (implies /F). |
| /offlinescanandfix | Runs an offline browse and ready on the volume. |
| /freeorphanedchains | FAT/FAT32/exFAT just: Frees whatsoever orphaned cluster chains instead of recovering their contents. |
| /markclean | FAT/FAT32/exFAT only: Marks the volume clean if no corruption was detected, even if /F was not specified. |
The /I or /C switch reduces the amount of fourth dimension required to run Chkdsk by skipping certain volume checks.
Source: https://www.geeksinphoenix.com/blog/post/2015/07/02/how-to-check-your-drive-for-errors-in-windows-10
Posted by: petersonhorms2000.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Find Errors In Windows 10"
Post a Comment